Sodium dihydrogen pyrophosphate
- Sodium acid pyrophosphate
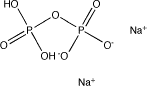
Sodium dihydrogen pyrophosphate | |
| |
| Formula | Na2H2P2O7 |
| Structure |  |
| Description | White odorless powder |
| Uses | Electroplating, metal cleaning and phosphatising, drilling muds, baking powders and leavening agent, buffer, sequestrant, peptising agent in cheese and meat products, frozen desserts. |
Registry Numbers. | |
| CAS | 7758-16-9 |
| EINECS | 231-835-0 |
| RTECS | UX6475000 |
| Merck Index | 8713 |
| 7758-16-9 is listed on the TSCA. | |
Chemical and physical properties. | |
| Formula mass | 221.94 |
| Melting point, °C | 220 (decomposes) |
Hazards and protection. | |
| Storage | Store in a cool, dry location in a tightly sealed container. |
| Handling | Containers of this material may be hazardous when emptied. Since emptied containers retain product residues (vapor, liquid, and/or solid), all hazard precautions given in the data sheet must be observed. |
| Protection | Wear safety glasses in compliance with OSHA regulations. Wear resistant gloves such as neoprene. Wear normal work clothing covering arms and legs. |
| Respirators | If needed, use a NIOSH/MSHA jointly approved dust respirator. |
| Small spills or leaks | Small Spill - Sweep up material for disposal or recovery. Large Spill - Shovel material into containers. Thoroughly sweep area of spill to clean up any residual material. |
| Stability | Stable at normal temperatures and pressures. |
| Incompatibilities | Strong mineral acids. |
| Hazardous Decomposition | Phosphorous compounds. |
Fire related information. | ||||
| Fire fighting | Wear a self-contained breathing apparatus with a full facepiece operated in the positive pressure demand mode with appropriate turn-out gear and chemical resistant personal protective equipment. Extinguish fire using most appropriate media. | |||
| Combustion products | Phosphorous compounds. | |||
Health related information. | |
Exposure effects | |
| Signs and symptoms of exposure to this material through breathing, swallowing, and/or passage of the material through the skin may include: stomach or intestinal upset (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) | |
| Ingestion | Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea are common, leading to dehydration. |
| Inhalation | Hyperventilation may occur secondary to hypocalcemia. |
| Skin | May cause mild skin irritation. Symptoms may include redness and burning of skin. |
| Eyes | Can cause eye irritation. Symptoms include stinging, tearing, redness, and swelling of eyes. |
| First aid | |
| Ingestion | Seek medical attention. If individual is drowsy or unconscious, do not give anything by mouth; place individual on the left side with the head down. Contact a physician, medical facility, or poison control center for advice about whether to induce vomiting. If possible, do not leave individual unattended. |
| Inhalation | If symptoms develop, move individual away from exposure and into fresh air. If symptoms persist, seek medical attention. If breathing is difficult, administer oxygen. Keep person warm and quiet; seek immediate medical attention. |
| Skin | Remove contaminated clothing and wash exposed area thoroughly with soap and water. A physician should examine the area if irritation or pain persists. |
| Eyes | Irrigate exposed eyes with copious amounts of tepid water for at least 15 minutes. If irritation, pain, swelling, lacrimation, or photophobia persist, the patient should be seen in a health care facility. |